Asst. Prof. Dr. Heba Jabbar Aleqabie
Prof. Dr. Asia Mahdi Naser Alzubaidi
Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology
How we connect, share, and communicate with one another has been profoundly altered by the widespread use of social media platforms. It’s possible that using social media has a harmful effect on our mental health, but research on the subject is currently limited (Fardouly et al., 2018).
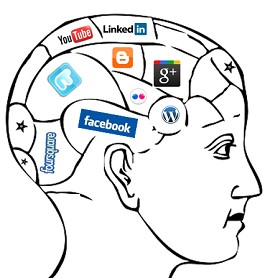
As seen in Figure 1, the psychology of social media is multifaceted and includes concepts like self-worth, social comparison, and addiction.
Figure 1. The social media affects(Halina 2019).
Social media platforms allow us to display ourselves to others specifically, influencing our feelings of self-worth. This might result in “social comparison,” in which we compare ourselves to others based on their online presence and feel inadequate or superior. According to the findings of certain studies, engaging in comparison on social media can result in unfavorable outcomes including despondency, anxiety, and a diminished sense of one’s own worth (Fardouly et al., 2018).
Additionally, it is worth noting that social media platforms are intentionally engineered to foster addictive behaviors. According to (Kuss and Griffiths 2017), the use of techniques such as notifications and likes can stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain, which may result in the development of compulsive usage patterns and potential addiction in some instances. Because of the addictive aspects that are inherently present in the use of social media, there is an option that this might have a harmful influence on a person’s mental health. The overutilization of social media has also been associated with various adverse consequences. Insufficient sleep quality (Levenson et al., 2016), worse academic achievement (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010), and heightened susceptibility to cyberbullying (Kowalski et al., 2014) are among possible ramifications associated with excessive engagement in social media platforms.
Gaining a comprehensive grasp of the psychological aspects of social media is crucial for individuals and organizations to make informed decisions pertaining to their online presence and use of these platforms. Despite the numerous benefits related with the utilization of social media, it is essential to maintain alertness of the possible adverse effects it might have on our mental well-being. The judicious utilization of social media and the mindful consideration of its impact on our cognitive and emotional states are crucial. The psychological ramifications of social media on society have garnered significant attention and scrutiny in recent years. The utilization of social media unquestionably results in the production of a number of benefits, some of which include the facilitation of interpersonal relationships and the improvement of communication. On the other hand, it is of the utmost importance to recognize the existence of negative effects, the likes of which have the ability to jeopardize the well-being of both individuals and society as a whole.
One of social media’s most well-known adverse effects is mental health. Researchers found that persons who spend a disproportionate quantity of time on social media are more prone to suffer anxiety, hopelessness, and loneliness. According to a Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology research, social media usage should be limited to 30 minutes each day. This dramatically reduced despair and loneliness. It’s possible that using social media can drive people to compare themselves to others in their social circles and harbor feelings of envy, which is another way in which social media can be harmful to a person’s mental health. People have a tendency to promote themselves in a favorable light on social media, and they frequently post about their triumphs, achievements, and pleasures. Research has proved this to be the case. This may cause other people to have feelings of inadequacy or jealousy, which is especially problematic if those other people already have difficulties with their own self-esteem.
Individuals are allocating an increasing amount of their time to engage with social media sites, including but not limited to Twitter, Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram. As a result, there has been an increase in addiction to these platforms. The dopamine hit that users get when they earn likes, comments, and shares on their postings is one of the primary causes of social media addiction. This produces an addicting sensation of affirmation and pleasure. Furthermore, social media allows users to disconnect from reality and communicate with others without leaving their homes.
It is possible that using social media would lead users to compare themselves to others in their social circles and experience feelings of envy. This is yet another potential adverse effect that using social media could have on a person’s mental health. On social media, people have a propensity to portray themselves in a positive light, and they regularly write about their wins, achievements, and pleasures. This has been demonstrated to be the case via research. This could give other people feelings of inadequacy or envy, which is troublesome in general but especially so if those other individuals already struggle with their own self-esteem issues.
In summary, the utilization of social media has fundamentally altered the manner in which individuals interact and communicate, but the psychological ramifications of its usage remain a subject of intense scholarly discourse. Various factors, such as social comparison and addiction, can significantly influence an individual’s mental well-being. There is a correlation between excessive usage of social media platforms and negative outcomes, including heightened susceptibility to clinical depression, anxiety, and compromised sleep quality. It is imperative for individuals and organizations to possess an understanding of these ramifications, exercise restraint in their utilization of social media, and accord significant importance to their psychological well-being. (Fardouly et al., 2018; Kuss & Griffiths, 2017; Levenson et al., 2016; Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Kowalski et al., 2014).
References:
⦁ Halina, Victoria. 2019. “The Psychology of Social Media — Why We Feel the Need to Share.” The Journal Blog. Retrieved May 26, 2023 (https://victoriahalina.medium.com/the-psychology-of-social-media-why-we-feel-the-need-to-share-18c7d2d1236).
⦁ Fardouly, J., Diedrichs, P. C., Vartanian, L. R., & Halliwell, E. (2018). Social comparisons on social media: The impact of Facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. Body image, 26, 38-45.
⦁ Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2017). Social networking sites and addiction: Ten lessons learned. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(3), 311.
⦁ Levenson, J. C., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., & Primack, B. A. (2016). The association between social media use and sleep disturbance among young adults. Preventive medicine reports, 5, 113-118.
⦁ Kirschner P.A., Karpinski A.C.(2010) Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior26(6):1237–1245
⦁ Kowalski RM,Limber SP,Aguilar-Raab C.(2014) Cyber bullying among college students: prevalence and demographic differences. Computers in Human Behavior35:363–373